The following information does not replace a physician’s diagnosis and advice under any circumstances whatsoever.
Lymphoedema
Lymphoedema: What’s that?
A lymphoedema is a chronic swelling which is incurred when the lymphatic fluid which is normally transported away by the lymphatic system accumulates in the tissue. This happens because the lymphatic system is disturbed or overburdened. A lymphoedema can be incurred on the arms, legs or other parts of the body and causes swelling, a feeling of tension and skin changes.
Digression: The lymphatic system
The lymphatic system is an important part of the human body and runs parallel to the blood circulation. It filters part of the blood plasma into a separate vessel system and forms the so-called lymph. This clear liquid is guided through lymph nodes on its way back to the trunk of the body, which filter out harmful substances and have them fought by defence cells.
The lymphatic system has important functions, including the transport of defence cells, nutrients and metabolic products as well as the drainage of excess tissue fluid.
The lymph is then finally returned to the subclavian vein. An interruption of the return transport can lead to lymph accumulation.
The lymph system (shown in green here) originates in the capillary area. On its path, the lymph passes through lymph nodes and flows into the venous system in the upper body.


Schematic depiction of lymph emergence via blood plasma filtration in a lymph vessel

Schematic depiction of a lymph node which fulfils an important immune defence task by filtering harmful substances out of the lymph

Lymphatic fluid is received by a lymphatic vessel and transported towards the trunk of the body
Our lymphatic system’s central task is the transport function of defence cells (immune defence), nutrients as well as the metabolism and waste products.
Furthermore, our lymphatic system drains off unnecessary tissue fluid.
The basis for these functions is unproblematic return transport of the lymph arising to the trunk of the body (upper body). The lymph is transported to the subclavian vein and returned to the body circulation. If the return transport of our lymph is disturbed, it can accumulate pathologically, resulting in fluid retention with tissue swelling. A lymphoedema arises.
Lymphoedema causes
Depending on its causes, the lymphoedema can be distinguished as primary or secondary.
Primary lymphoedema:
The primary lymphoedema is always caused by a hereditary dysplasia (anomaly) of the lymph vessels or lymph nodes.
Its appearance may be pronounced directly after birth or manifest themselves at a later point in time.
- Hereditarily caused dysplasia
- Sporadic abnormal development of the lymph system such as:
- Hyperplasia (enlargement of an organ)
- Hypoplasia (underdevelopment of an organ)
- Aplasia (non-development of an organ)
- Dysplasia (malformation of an organ)
Secondary lymphoedema:
A secondary lymphoedema is normally triggered by external/acquired influences:
- Infectious diseases
- Insect bites
- Swelling of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis)
- Pathological compression of the lymph vessels (e.g. by a tumour)
- Removal of lymph nodes within the course of tumour therapy
- Traumas/Accidents
- Injuries to the lymph tracts (e.g. due to radiation)
These deformations and illnesses result in pathologically changed lymph flow, thus causing congestion in the lymph vessels. This congestion is incurred as an oedema on the extremities (distally of the damages, e.g. on the legs).
Secondary lymphoedema occur more frequently than primary oedema (approx. 10:1) and are frequently localised single-sided.
Considerably more women than men develop a lymphoedema. In particular, breast cancer patients can be affected by a lymphoedema following their illness or treatment. Axillary lymph nodes are often removed in connection with breast cancer therapy. The lymphatic fluid can no longer be drained here. As a consequence, it congests in the vessel (here the arm). The vascular wall cannot bear this increased pressure in the long-term and the lymph escapes into the tissue.

Pathological depiction of a lymphatic vessel:
Pathological narrowing
Vessel valve malformation → Lymph congestion
Lymphoedema symptoms
The cause of the symptoms of a lymphoedema is the retention of lymphatic fluid in the tissue.
This can best be observed on the extremities (arms and legs/feet). One reason for this can be the impaired return transport of the lymph against gravity.
Lymphoedema often develop insidiously, as they initially do not cause any pain.
Based on the symptoms, the lymphoedema can be categorised with 4 stages:

Latency stage
-
Lymphoedema is not visible
-
Isolated lymph vessels are already affected, but can be diverted through healthy lymph tracts
-
Persons affected do not yet have any symptoms

Spontaneously reversible stage
-
Oedema has a soft consistency
-
Elevation reduces the swelling

Stage not spontaneously reversible
-
Oedema with secondary tissue changes, such as hardening
-
Elevation does not eliminate the swelling

Pronounced form of the stage which is not spontaneously reversible
-
The scope has increased considerably with overhanging skin flaps
-
In-part with typical skin changes such as significantly hardened skin, development of vesicles and fistulae
-
Elephantiasis
As the swelling causes skin pressure, the tissue is undersupplied because small blood vessels are suppressed. As a consequence, skin hardening in connection with impairment of wound healing is often experienced in advanced stages.
Moreover, the skin can no longer fulfil its natural immune function, resulting in increased risk of infection in this area.
Lymphoedema diagnosis
In addition to case history and family history, physical inspection and palpation (feeling) play an important role. Various tests such as the Stemmer sign exist. It is deemed positive if no lifting of a skin fold on the forefoot/toes is possible.
A flat skin dent which remains when the skin is pressed in is equally typical for a lymphoedema in its initial stage.
Positive Stemmer sign:

If the skin cannot be lifted over the 2nd toe, this may indicate a lymphoedema.
Skin dent (pitting oedema)

Skin pressure enables displacement of the congested lymphatic fluid and a temporary dent remains.
Imaging procedures such as ultrasound or a lymph angiography can be used to depict and examine the lymph vessels and lymph nodes. Equally, congested tissue fluid can be recognised there.
The appearance of the chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is very similar to the lymphoedema’s. Here, the treating physician will try to delimit this.
How can you prevent a lymphoedema?
Frequently, it is not possible to hinder a lymphoedema with preventive measures. The ailment is often incurred after necessary operations or results from hereditary vessel malformation.
Nonetheless, we can support our lymph system actively:
- Appropriate physical activity which is gentle on the joints such as swimming and jogging supports the physiological lymph return transport.
- Reduce excess weight. Weight reduction in case of excess weight reduces the pressure affecting the lymph vessels.
- Close-fitting/incisive clothing should be avoided as it can constrict the lymph vessels.
- Hot baths/saunas and intense exposure to the sun can dilate the vessels and additionally impede the natural lymph return flow.
Differentiation lymphoedema vs. lipoedema
Lymphoedema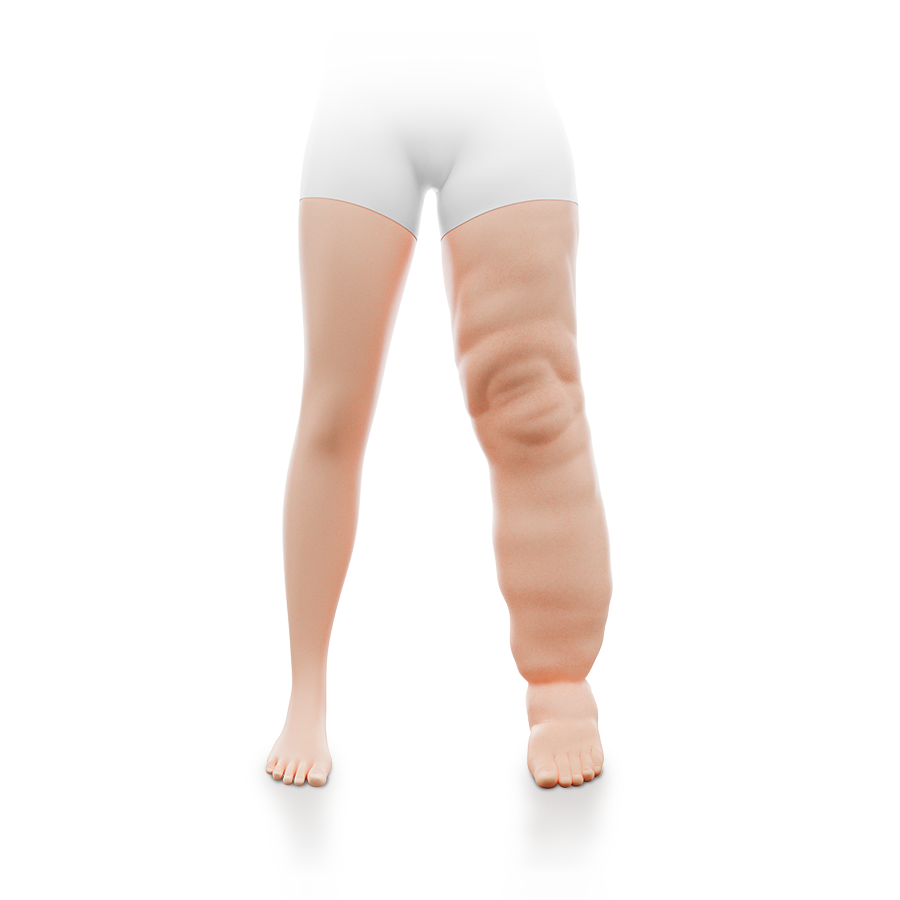
|
Lipoedema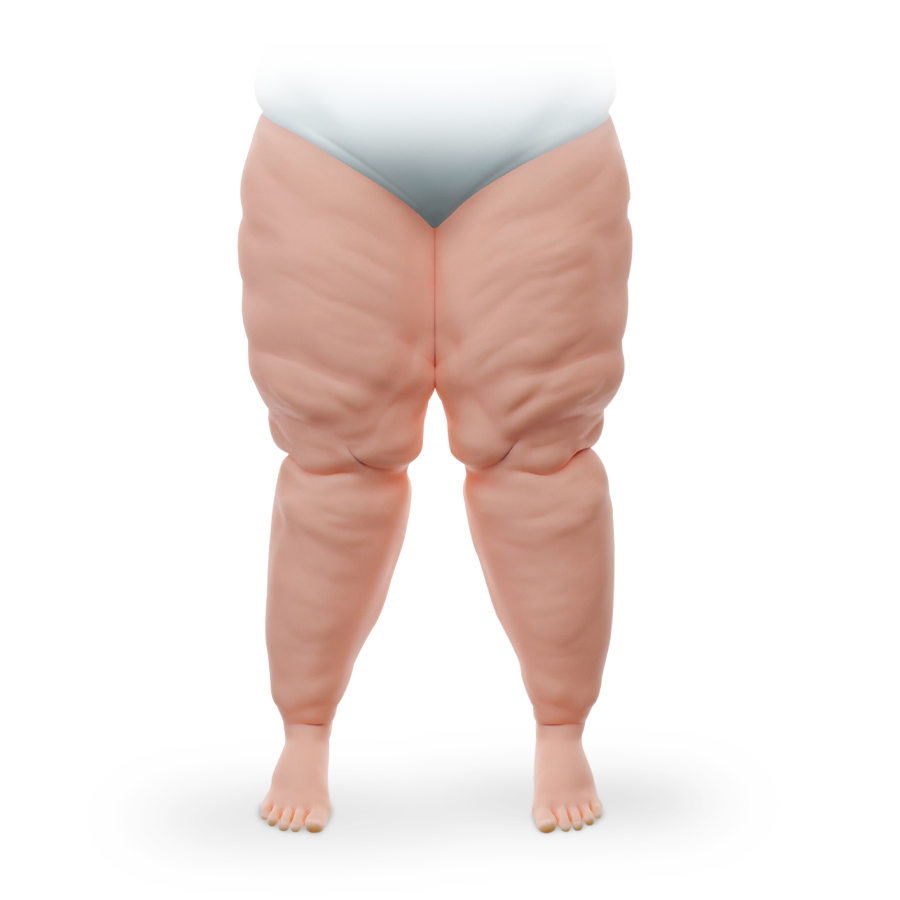 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Stemmer sign | ✓ | x |
| Skin dent test (Pittingödem) |
✓ | x |
| Pressure pain | x | ✓ |
| Symmetry | x | ✓ |
| Inclination to hematoma | x | ✓ |
| Back of the foot/ hand affected | ✓ (possible) |
x (not normally) |
Lymphoedema therapy
Early therapy is required, as the swellings can otherwise become very pronounced during the further course of the disease and cause skin changes.
Conservative therapy:
Wearing medical compression stockings is a component of Complex Physical Decongestion Therapy, which is used as a proven treatment method for oedema ailments. It consists of five modules which are applied in two stages:
During manual lymph drainage, the tissue is decongested with a special massage, i.e. the flow of the lymphatic fluid is activated. This enables the regression of the lymph oedema.
Medical compression stockings, which can considerably reduce or even hinder renewed fluid accumulation in the tissue during the maintenance stage are a further important therapeutic component. When worn, interplay between the muscles, skin and pressure exerted by the knitted fabric takes place.
This therapy is applied for patient treatment at an early stage of the illness
Surgical therapy
If conservative therapy achieves no improvement, the treating physician can consider surgical therapy.
For example, it is possible to connect a congested lymphatic vessel and a close-by vein, enabling the lymph to drain off via the vein.
Furthermore, healthy lymph nodes/lymph tracts can be transplanted from an appropriate body region. Lymph nodes have the property that they form their own new lymph tracts, via which the congested lymph can drain off.
The treating physician decides on the necessity and appropriate operational proceedings.
BORT AktiVen® Intense
Medical compression stockings
A large number of individual versions for leg, hand and toe care excel with their top manufacturing quality. Available in different versions as well as standard and trend colours, they are an attractive and medically effective accompaniment for oedema therapy.
Daily wearing for relief you can feel
In order to generate the best possible therapeutic success, medical compression stockings should be put on daily after getting up and be worn until the evening during the maintenance stage.
The stockings are adapted individually to the legs, arms or hands and are therefore very comfortable to wear.



